Everytime I add new sources to Gemini it generates evrn better brief video explanations. This latest one is excellent.
Everytime I add new sources to Gemini it generates evrn better brief video explanations. This latest one is excellent.

Posted in Debt, Finance and Economics, Geopolitics
Tagged credit clearing, Keynes, money problem
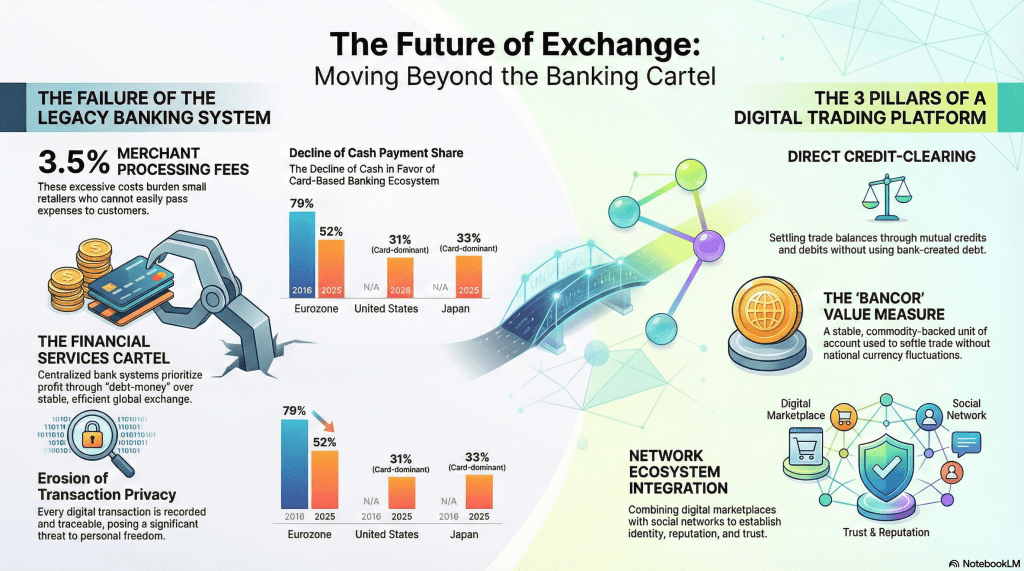
Yesterday I posted a remarkable six minute video that does an excellent job of explaining what I propose in Chapter 19—The Role of Governments in Solving the Money Problem, of my revised edition of my book, The End of Money and the Future of Civilization. The video below, which was also generated by NotebookLM, is based on additional material from my book and focuses on the nature of the money problem and how it has developed over more than 300 years. I am now working on the next video which will concentrate on explaining the solutions and alternative exchange devices and systems that I have long been prescribing. Watch for it.
Posted in Banking, credit, Debt, Geopolitics
Tagged usury, interest, bank of england, Federal Reserve, bank war
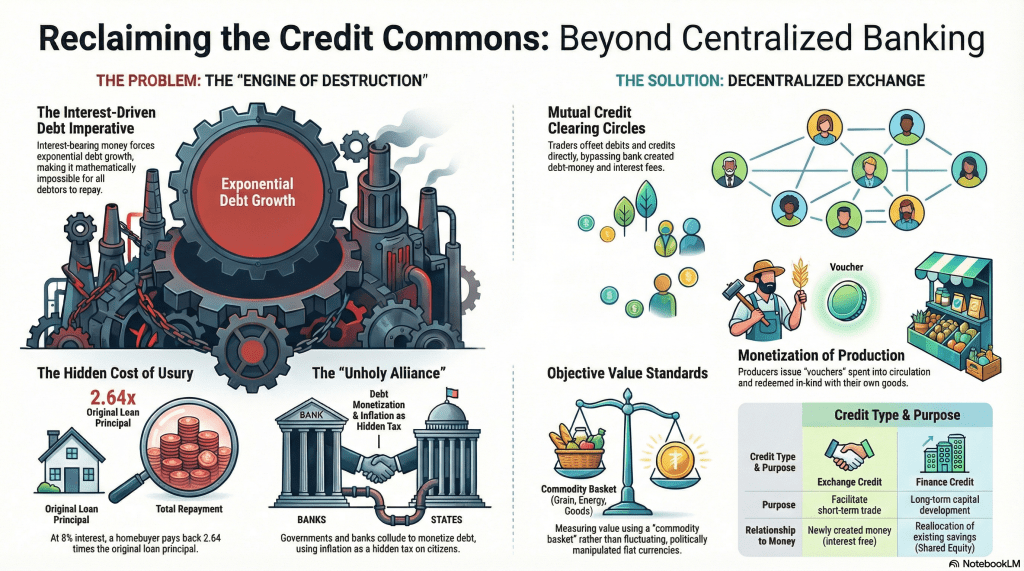
John Mauldin’s recent article, Late Summer Sandpile, is one of his best–thought-provoking and very timely. As an investment advisor, his primary concern is with financial markets and systems, but the academic research findings in complexity and systems theory have a broader relevance. Thinking about systems as sand piles, academics can examine the dimensions of stability and instability as they occur in a wide variety of systems. After reading the article, I felt inclined to respond. Here below is what his article evoked in me.
Our civilization “sand pile” is comprised of many diverse but related fingers of instability, some small, some large, and many interconnected; that puts our entire civilization at risk. Among the most worrisome features are the astronomical growth of debt, religious, and cultural conflicts, competing political ideologies, and international intrigues and violence involving players that are now in command of unprecedented destructive power. If the conflict between Ukraine/NATO and Russia doesn’t trigger a nuclear war in the near term as Peter Koenig expects, the mountains of debt being built up will trigger a global financial collapse in the not-too-distant future. Markets are much more centralized than they used to be and are increasingly dominated by a few major players which tosses free market theories of market behavior out the window. Virtually all markets today are manipulated by huge corporations, investment funds, and asset management firms. But the biggest manipulators are the national governments of the major powers and their partners who run the global banking cartel. The top dog among them is the US government which has greatly abused the status of the dollar as the world’s reserve currency. It doles out privileges not only via legislation and executive orders, but increasingly by the preferential expenditure of massive amounts of legalized counterfeit money to favored clients and proxy governments in a desperate attempt to preserve and extend its “full spectrum dominance,” and replace democratic national governments with a One-World neo-feudal world order. The US and its allies are pushing the limits in the hope and expectation that there will not be a reaction big enough to upset their apple cart. But as Mauldin reminds us, one small grain of sand is often all it takes.
# # #
Posted in The state of democracy, Debt, Geopolitics
Tagged collapse, war, instability
This is the latest chapter to be published of my new 2024 edition of The End of Money and the Future of Civilization. It continues the story begun in the previous chapter of how money has evolved and changed its character over time.
Here is a brief excerpt:
Money has become merely an accounting system, a way of “keeping score” in the economic “game” of give and take. —Thomas H. Greco, Jr.
Let us begin by summarizing the evolution of the various kinds of money that have been used to mediate reciprocal exchange:
For now, you can read or listen to the entire chapter at Future Brightly:
Chapter 10—The Third Evolutionary Stage—The Emergence of Credit Clearing-Text
Chapter 10—The Third Evolutionary Stage—The Emergence of Credit Clearing-Audio narration
It will also be published soon here, and on my own Substack channel. Further chapters will continue to be posted as they are completed. Watch for Chapter 11 to be posted soon.

As always, your comments and suggestions are welcomed,
Thomas
Posted in Banking, Debt, money, credit
Tagged money, credit clearing, currency, fiat money
Erecting the ‘wall of separation between church and state’… is absolutely essential in a free society.
— Thomas Jefferson
The established beliefs about money in today’s world have become a sort of religion in which a fundamental tenet holds that government must, either directly or indirectly, have power over the system of money creation and circulation. This erroneous belief has taken the world to the brink of disaster which will surely ensue unless we take steps to depoliticize money by achieving the separation of money and state.
It should be obvious by now that there will never be peace in the world so long as those who control our national governments are able to conjure up out of thin air the seemingly endless amounts of pseudo-money they need to pay for wars and whatever else might bolster their political and economic interests.
Read all about it in Chapter8—The Separation of Money and State, the latest chapter to be published in my new 2024 edition of The End of Money and the Future of Civilization.
You can find it right now on Future Brightly, and it will be published soon here and on my own Substack channel.
Further chapters will continue to be posted as they are completed. Watch for Chapter Nine to be posted soon.
As always, your comments and suggestions are welcomed,
Thomas
Posted in Banking, credit, Debt, Emerging paradigm, Freedom, Geopolitics, money
Tagged centralization, credit, decentralization, free exchange, legal tender, measure of value, peace, power, war
Anyone who believes exponential growth can go on forever in a finite world is either a madman or an economist. —Kenneth Boulding, Economist
Chapter Six — Usury, the Engine of Destruction, of The End of Money and the Future of Civilization, new 2024 edition, is now available at Ken Richings; Substack channel, Future Brightly. in advance of its publication here on my website and elsewhere. Access to my work remains free, but please reward Ken for his good work by opting to take a paid subscription to his Substack channel.
Further chapters will continue to be posted as they are completed on Future Brightly, and two weeks later on this and the other sites. Watch for Chapter Seven to be posted in about two weeks.
As always, your comments and suggestions will be welcomed,
Thomas
___________________

Chapter Six, Usury, Engine of Destruction-Text
Chapter Six, Usury, Engine of Destruction-Audio narration
Posted in Basic Concepts, Debt, Inflation, The Debt Imperative
Tagged budget deficit, growth imperative, interest, national debt, usury
Thomas H. Greco, Jr. Interview with Bruce de Torres, on his Worldstage show on TNT Radio:
Covering the history of centralized banking, the danger of today’s concentration of wealth in the hands of a few who are working to completely control humanity; and the need to reinvent money, devolve power to local communities, and create honest “home-grown” means of payment (liquidity). His highly acclaimed book, The End of Money and the Future of Civilization, is being revised, updated, and expanded to reveal how the dysfunctional money system operates, and how to reinvent money to enable the honest exchange of value. New chapters are being posted serially on Future Brightly, on his website, as well as on his Substack and Medium channels. Almost all his writings and accumulated resources for researchers and monetary innovators can be downloaded free at BeyondMoney.net.
You can view or download the video here or on Podbean
Or listen to or download the audio at Podbean or on beyondmoney.net
Last year (2021) I gave a three part webinar presentation for The Henry George School of Social Science. In case you missed it, here is the description and the link to the recorded sessions. For each part you will find a list of recommended resources and references.
Our Money System – What’s Wrong with it and How to Fix it
A critical look at the present global system of money and banking, how it has evolved, why it is problematic, and where it is trending.
The series will also look into past, present, and future exchange and payment alternatives, like Depression-era script, local and private currencies, commercial trade exchanges and LETS systems that apply the “credit clearing” process, and the more recent emergence of crypto-currencies and blockchain ledgers and their potential role. It will include discussion of how these have evolved, their advantages, limitations and future potential and what needs to be done to take them to scale, their political and economic implications, and innovations that are making conventional money obsolete.
WHAT is money?
WHY do we need money?
WHAT is wrong with our money system?
Can we live without money?
HOW can business be conducted without money?
What are the economic, social and political implications of monetary policies and systems?
What is the likely impact of present day monetary innovations?
May 21 – Session 1 provided an overview of the present system of money and banking, how it has evolved, how and why it is problematic, and where it is trending. I spoke about the interest-based debt-money system, how it causes the growth imperative and the politicization of finance and exchange, and the political and economic consequences of its continuation. I outlined the fundamental concepts of exchange and finance and the principles upon which sound and sustainable systems are being developed. Participants were asked to read or listen to some specific materials in preparation of the subsequent sessions.
June 4 – Session 2 was more interactive and provided ample opportunity to discuss questions that were evoked by the previous session and the assignments, including topics like inflation, depressions, asset bubbles and busts, the savings and investment functions, and government responses to shocks like the 2008 financial crisis and the more recent pandemic. This lead into discussion about possible solutions to the problems caused by the present system, and the role of local currencies and other alternatives for the exchange of value.
June 18 – Session 3 concentrated on past, present, and future exchange and payment alternatives, like Depression-era scrip, local and private currencies, commercial trade exchanges and LETS systems that apply the “credit clearing” process, and the more recent emergence of crypto-currencies and blockchain ledgers and their potential role. It included discussion of how these have evolved, their advantages, limitations and future potential and what needs to be done to take them to scale.
To round out your education you can also read my recent articles.
Continue… Our Money System – What’s Wrong with it and How to Fix it
# # #
This little vignette written by Don Werkheiser remains one of the best concise explanations of inflation I’ve ever seen. It was published in the spring 1982 edition of Green Revolution, the journal of the School of Living a non-profit organization with which I was associated throughout the 1980s and into the early 1990s. The story helps to elucidate the nature of the dysfunctional political money system that has plagued the world for hundreds of years, but in its brevity and simplicity neglects to mention another feature of the money system that adds to our misery; that is the fact that the “Mayor” and his friends do more than spend counterfeit money into circulation, they have also established “banks” and require that other people who need money to do business must borrow their pseudo-money into circulation and pay interest on it. That enables the bankers to extract even more wealth from the rest of the people while creating an unending and unsustainable expansion of debt. I have articulated that “debt-growth imperative” in my paper titled, the Usury Conjecture.
An Honest Money Would Stop Inflation by Don Werkheiser
A rural village has no money. All trade is by barter. A farmer comes to town and deposits 10 bushels of corn with a man who has a store room. This operator gives the farmer 10 receipts, each redeemable in a bushel of corn. But the farmer asks for receipts in smaller denominations. The storekeeper gives him 40 receipts for 40 pecks. The farmer trades ten of these corn-receipts for other products; they are each accepted at the value of a peck of corn. That acceptance constitutes the issue of corn notes as money.
Such receipts are generalized credit instruments. They refer to stored corn, but not to any specific peck of corn. When the seller wants a peck of corn the receipt is redeemed. Otherwise it is spent again, and ownership of a peck of corn is conveyed to the next seller. The next day the farmer returns to town and spends 10 corn notes (each of one peck of corn in value) for his wife’s birthday present. Now the farmer has doubled the money supply in circulation, but there is no inflation; there are redeemable goods back of them.
What then is inflation? We must understand “money” and the storekeeper’s actions.
The store room owner noticed that the corn notes were accepted in trade. So he made 40 more “peck-receipts” looking just like corn-receipts and then he spent them into circulation. That is inflation–counterfeit receipts passed as valid receipts. Assume that the counterfeit receipts were accepted at face value. In that case, the counterfeiter effected a robbery of commodities equal in value to 40 packs of corn, while those who accepted them received receipts which measured the extent to which they had been robbed. So long as confidence lasts, the game would continue and receipts could be spent. New sellers would be holding empty receipts. The game would collapse when all the corn in the warehouse was redeemed, and holders of the 40 counterfeit receipts found no one who would take them in trade.
Worse could happen if the counterfeiter had the skills of a politician. If, when confronted by angry holders of his counterfeit receipts he declared himself a benefactor of the community–and showed that the original issue by the farmer was too limited, and that his own issues stimulated industry and trade (he would not mention that the farmers issue was redeemable while his own was not). He noted that most people did not want corn; they wanted a medium of trade that they could use to speed up trade.
More to come.
They were told: “If the game stopped then, the holders would be losers, but if they continued, they could all buy what they wanted. In fact if they elected him Mayor he would declare pseudo-corn-notes to be legal tender, and he’d also begin a program of public works. Soon everyone would be rich.” An ignorant public agreed.
Elected Mayor, the counterfeiter issue another stock of corn-notes called “pecks” and declared them to be worth a peck of corn in the market (but not anywhere redeemable). On each note was a picture of a peck-basket, but what it contained was not specified. Just a peck of value.
The “pecks” circulated and trade increased. Then a strange thing happened. The Mayor and his agents could outbid everybody for produce and services. They also controlled the printing presses for printing “pecks.” Prices were bid up on the things the Mayor’s group approved. Workers and businessman migrated into those industries for wages and profit. The stock of other things became short. Everyone couldn’t buy what they wanted. People threatened to recall the Mayor if he didn’t improve things. So he issued more “pecks” and then more and more.
The more money people had, the less they could buy. Only the Mayor and his friends had enough — rather too much — money. They gave expensive parties, bought votes, hired police and soldiers; and gave everyone a vested interest in continuing the game, through welfare, social security, profitable contracts, and “peck-funded” jobs.
Confusion resulted. It is evident there are two kinds of money: honest redeemable money and inflatable unredeemable money. These keep our economy teetering between “prosperity” and “depression.” Have we any proof that those in charge of our money system intend to create an honest system? That would break their power. A sound alternative is for people to operate their own money system. American and world history have produced workable patterns; some are underway today.
# # #
Take note that the story does not mention any need for gold or silver backing for money to be honest. As E.C. Riegel makes plain in his book, Private Enterprise Money, “When businessmen resolve to set up a money system, they agree to hold in trust for each other goods and services that are pledged against the drafts which they have issued in the form of money. These values — that are held in trust by all for any who may present a money draft therefore — constitute a vast pool, not housed at one place, but scattered throughout the trading sphere. This vast pool of goods and services is the basis or backing for the outstanding money supply. “Reserves” and metal hoards are but window dressing. Only that which is purchasable is back of money.”
To learn more about honest and effective forms of money and how to create them, see my books, The End of Money and the Future of Civilization, and, Money: Understanding and Creating Alternatives to Legal Tender.